A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, is a serious condition that can lead to severe complications if left untreated. While it may start as a minor toothache, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, potentially becoming life-threatening. Understanding the timeline and risks associated with a tooth infection is crucial for seeking timely medical intervention. This article explores the progression of a tooth infection, the potential complications, and how long it might take for a tooth infection to become fatal.
What is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria invade the dental pulp, the innermost part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. This can happen due to untreated tooth decay, a cracked tooth, or gum disease. The infection leads to the formation of pus, which collects in the tooth or surrounding tissues, causing pain, swelling, and other symptoms.
There are three fundamental sort of dental abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: This occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root and is usually the result of untreated dental caries (cavities) that allow bacteria to reach the pulp.
- Periodontal Abscess: This type of abscess forms in the gums and is often associated with gum disease.
- Gingival Abscess: This is an abscess that forms in the gum tissue without affecting the tooth or periodontal ligament.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
The symptoms of a tooth infection can vary depending on the severity and location of the abscess. Common symptoms include:
- Severe, throbbing toothache that may radiate to the jawbone, neck, or ear.
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
- Swelling in the face, cheek, or lymph nodes.
- Fever.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing.
- A foul taste in the mouth or bad breath.
- General feeling of being unwell.
How Does a Tooth Infection Spread?
A tooth infection can spread beyond the tooth and gums if left untreated. The infection can travel through the bloodstream or the surrounding tissues, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions. The spread of infection can occur in several ways:
- Local Spread: The infection can spread to nearby tissues, such as the jawbone, sinuses, or soft tissues of the face and neck. This can lead to cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection, or Ludwig’s angina, a severe infection of the floor of the mouth.
- Systemic Spread: If the infection enters the bloodstream, it can lead to sepsis, a condition where the body’s immune system overreacts to the infection, causing widespread inflammation and organ failure.
- Distant Spread: In rare cases, the infection can spread to distant parts of the body, such as the heart (endocarditis), brain (abscess), or lungs (pneumonia).
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Becomes Life-Threatening?
The timeline for a tooth infection to become life-threatening varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s overall health, the severity of the infection, and how quickly treatment is sought. However, in general, a tooth infection can become dangerous within a matter of days to weeks if left untreated.
- Initial Stage (1-3 days): In the early stages, the infection is localized to the tooth and surrounding tissues. Symptoms may include a mild to moderate toothache, sensitivity, and slight swelling. At this stage, the infection is usually treatable with antibiotics and dental procedures such as a root canal or extraction.
- Progression (3-7 days): If the infection is not treated, it can spread to the surrounding tissues, causing increased swelling, pain, and fever. The infection may also begin to affect the lymph nodes, leading to swelling in the neck and jaw. At this stage, the risk of complications such as cellulitis or Ludwig’s angina increases.
- Severe Stage (1-2 weeks): By this point, the infection may have spread to other parts of the body, leading to systemic symptoms such as high fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. The risk of sepsis, a life-threatening condition, becomes significant. Sepsis can develop rapidly, often within hours or days, and requires immediate medical attention.
- Critical Stage (2+ weeks): If the infection continues to spread untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as brain abscess, endocarditis, or pneumonia.
It is important to note that the timeline can vary widely depending on the individual. Some people may experience rapid progression of the infection, while others may have a slower progression. However, the risk of serious complications increases the longer the infection is left untreated.
Complications of a Tooth Infection
A tooth infection can lead to several serious complications if not treated promptly. Some of the most dangerous complications include:
- Sepsis: Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to an infection, leading to widespread inflammation and organ failure. Sepsis requires immediate medical treatment, often in an intensive care unit.
- Ludwig’s Angina: Ludwig’s angina is a severe infection of the floor of the mouth and neck. It can cause swelling that obstructs the airway, making it difficult to breathe. This condition requires emergency medical treatment, often including surgery to drain the abscess and antibiotics to treat the infection.
- Brain Abscess: In rare cases, a tooth infection can spread to the brain, leading to the formation of an abscess. A brain abscess is a collection of pus in the brain that can cause symptoms such as headache, fever, nausea, and neurological deficits. This condition requires immediate medical attention and often involves surgery to drain the abscess.
- Endocarditis: Endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves. It can occur when bacteria from a tooth infection enter the bloodstream and attach to damaged areas of the heart. Symptoms of endocarditis include fever, fatigue, and heart murmurs. This condition requires long-term antibiotic treatment and, in some cases, surgery.
- Osteomyelitis: Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, which can occur if a tooth infection spreads to the jawbone. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and fever. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and, in some cases, surgery to remove infected bone tissue.
Risk Factors for Severe Complications
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing severe complications from a tooth infection. These include:
- Delayed Treatment: The longer a tooth infection is left untreated, the greater the risk of complications. This is very good treatment .
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk of developing severe complications from a tooth infection.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene can increase the risk of tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to tooth infections.
- Smoking: Smoking can impair the body’s ability to fight infections and can increase the risk of complications from a tooth infection.
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infections.
Treatment of a Tooth Infection
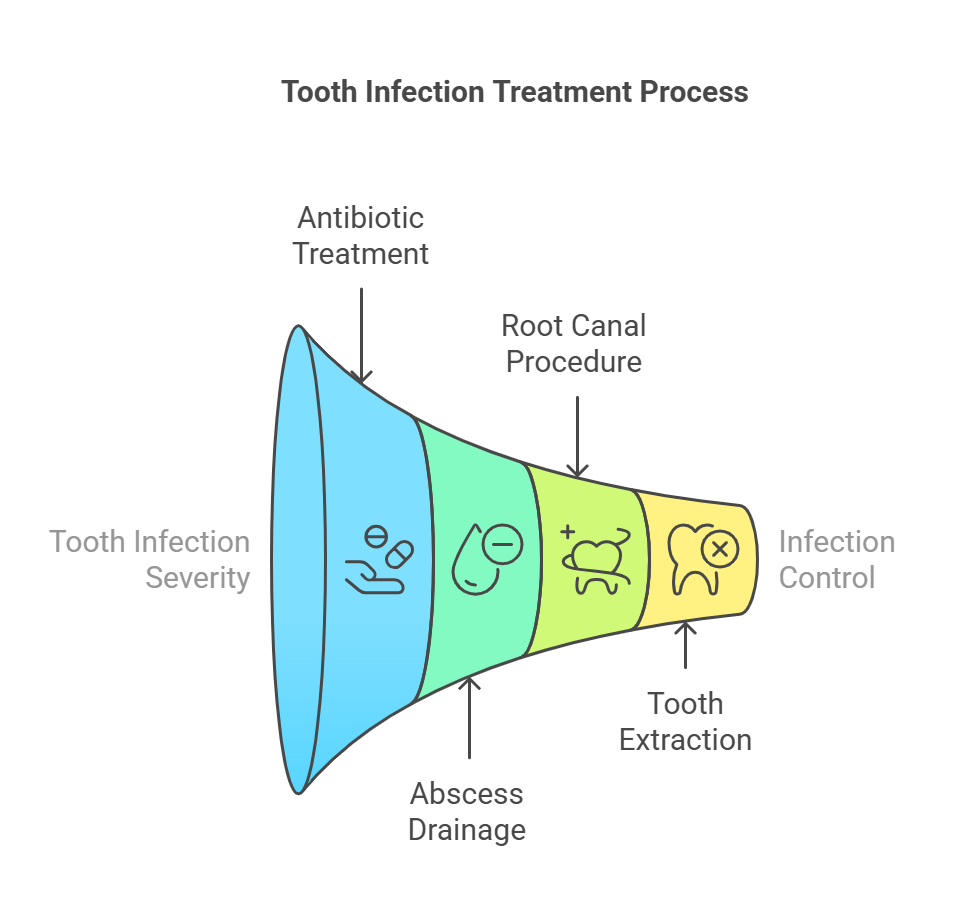
The treatment of a tooth infection depends on the severity of the infection and the extent of its spread. Common treatments include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat the infection and prevent it from spreading. However, antibiotics alone are not usually sufficient to treat a tooth infection, and dental treatment is also required.
- Drainage: In cases where there is a significant collection of pus, the abscess may need to be drained. This can be done through a small incision in the gum or by performing a root canal to remove the infected pulp.
- Root Canal: A root canal is a procedure in which the infected pulp is removed from the tooth, and the inside of the tooth is cleaned and sealed.
- Tooth Extraction: In some cases, the infected tooth may need to be extracted to prevent the infection from spreading. This is usually done if the tooth is severely damaged and cannot be saved with a root canal.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to treat complications such as sepsis, Ludwig’s angina, or a brain abscess. Treatment in the hospital may include intravenous antibiotics, surgery, and supportive care.
Prevention of Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections is key to avoiding the serious complications associated with them. Some steps you can take to prevent tooth infections include:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Treat Dental Problems Promptly: If you have a toothache, sensitivity, or other dental problems, seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the problem from worsening.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of dental problems and weaken the immune system.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support overall health and reduce the risk of dental problems.
Conclusion
A tooth infection is a serious condition that can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. The timeline for a tooth infection to become fatal can vary, but the risk of severe complications increases the longer the infection is left untreated. Seeking prompt dental care is essential to prevent the infection from spreading and to avoid serious health consequences. By practicing good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and treating dental problems promptly, you can reduce the risk of developing a tooth infection and protect your overall health. If you suspect you have a tooth infection, don’t wait—seek medical attention immediately. Your health and well-being depend on it.
FAQs
1. How long does it take for a tooth infection to become dangerous?
A tooth infection can become dangerous within a few days to a couple of weeks if left untreated. The infection can spread from the tooth to surrounding tissues, the jawbone, and even into the bloodstream, leading to severe complications like sepsis, Ludwig’s angina, or brain abscess. The exact timeline depends on factors such as your immune system, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and whether you have underlying health conditions.
2. Can a tooth infection kill you?
Yes, a tooth infection can kill you if it spreads to other parts of the body. Complications such as sepsis (blood infection), Ludwig’s angina (a severe neck and throat infection), or brain abscess can be fatal if not treated promptly. While death from a tooth infection is rare in modern times due to antibiotics and dental care, it is still a possibility if the infection is ignored.
3. What are the signs that a tooth infection is spreading?
Signs that a tooth disease is spreading incorporate:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing (a sign of Ludwig’s angina).
- High fever and chills.
- Rapid heart rate or confusion (possible signs of sepsis).
- Fatigue or feeling extremely unwell.
4. How long can you live with an untreated tooth contamination?
There is no exact timeframe, but an untreated tooth infection can become life-threatening within weeks to months. In some cases, severe complications like sepsis can develop within days. The risk of death increases the longer the infection goes untreated, especially if it spreads to vital organs or the bloodstream.
5. What factors affect how quickly a tooth infection becomes dangerous?
Several factors influence the progression of a tooth infection:
- Immune system strength: People with weakened immune systems (e.g., due to diabetes, HIV, or chemotherapy) are at higher risk of rapid infection spread.
- Type of bacteria: Some bacteria are more aggressive and can cause faster tissue damage.
- Access to dental care: Delaying treatment allows the infection to worsen.
- Overall health: Chronic conditions like heart disease or respiratory issues can increase the risk of complications.
6. Can antimicrobial halt a tooth disease from murdering you?
Antibiotics can help control the infection and prevent it from spreading, but they are not a cure on their own. If the infection has already spread to other parts of the body, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be required.
7. What are the foremost unsafe complications of a tooth contamination?
The most dangerous complications include:
- Ludwig’s angina: A severe infection of the floor of the mouth that can block the airway.
- Brain abscess: A rare but deadly complication where the infection spreads to the brain.
- Osteomyelitis: An infection of the jawbone that can lead to bone destruction.
8. How can I prevent a tooth infection from becoming life-threatening?
To prevent a tooth infection from becoming dangerous:
- Treat dental problems early: Don’t ignore cavities, cracked teeth, or gum disease.
9. What should I do if I suspect a tooth infection?
If you suspect a tooth infection:
- Contact your dentist immediately to schedule an emergency appointment.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen) to manage pain and reduce swelling.
- Avoid applying heat to the infected area, as this can worsen swelling.
- Seek emergency care if you experience difficulty breathing, swallowing, or signs of sepsis (e.g., high fever, rapid heart rate).
10. Is it possible to die from a tooth infection in 2025?
While modern medicine has made death from a tooth infection rare, it is still possible, especially in cases where treatment is delayed or the individual has underlying health conditions. Access to timely dental care and antibiotics significantly reduces the risk of fatal complications.
