Insurance is like a safety net for life’s uncertainties. It’s a way to protect yourself, your loved ones, and your belongings from unexpected events that could otherwise lead to financial hardship. At its core, insurance is about sharing risk. Instead of bearing the full brunt of a loss on your own, you pay a small amount (called a premium) to an insurance company. This simple yet powerful concept has become a cornerstone of modern life, offering peace of mind and financial security to individuals, families, and businesses alike.
Think of insurance as a promise—a promise that if life throws you a curveball, you won’t have to face it alone. Whether it’s a car accident, a medical emergency, or damage to your home, insurance ensures that you have the support you need to recover and move forward. It’s not just about money; it’s about stability, resilience, and the ability to bounce back when things don’t go as planned.
Life is unpredictable. No matter how carefully we plan, unexpected events can disrupt our lives in an instant. A sudden illness, a natural disaster, or an accident can lead to significant financial strain. Insurance acts as a buffer, absorbing the shock of these events and allowing you to focus on what truly matters—your health, your family, and your future.
For businesses, insurance is equally critical. It protects against risks that could otherwise cripple operations, such as lawsuits, property damage, or employee injuries. By transferring these risks to an insurance company, businesses can operate with confidence, knowing they have a safety net in place.
In essence, insurance is about hope and preparation. It’s about hoping for the best while preparing for the worst. It’s a tool that empowers individuals and businesses to take risks, pursue opportunities, and build a better future without fear of losing everything.
Types of Insurance
Insurance comes in many forms, each designed to address specific risks and needs. Here’s a closer look at the most common types of insurance and how they work:
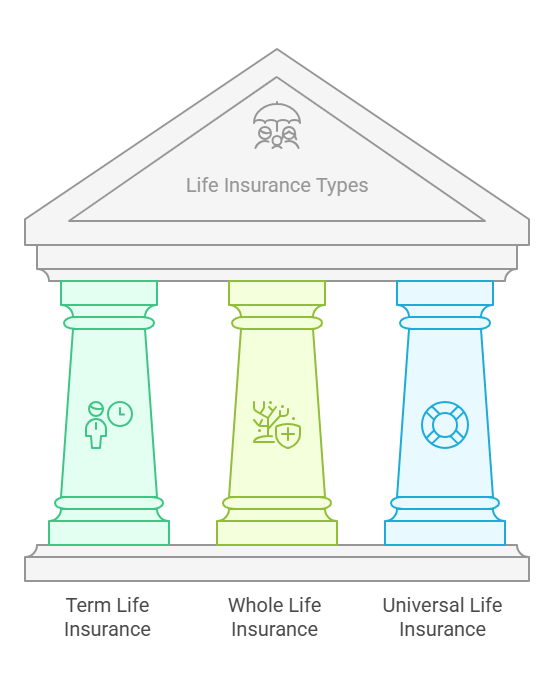
1. Life Insurance
Life insurance is a promise to your loved ones—a promise that they’ll be taken care of financially if something happens to you. It’s a way to ensure that your family can maintain their lifestyle, pay off debts, and cover expenses like education or funeral costs even in your absence.
- Term Life Insurance: This is the simplest and most affordable type of life insurance. It provides coverage for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If you pass away during the term, your beneficiaries receive a payout. If you outlive the policy, it expires unless you renew it.
- Whole Life Insurance: This type of insurance offers lifelong coverage and includes a savings component called cash value. Over time, the cash value grows, and you can borrow against it or withdraw funds if needed.
- Universal Life Insurance: A flexible option that allows you to adjust your premiums and death benefits. It also builds cash value, which earns interest over time.
2. Health Insurance
Health insurance is your shield against the high costs of medical care. It ensures that you can access the treatment you need without worrying about the financial burden. From routine check-ups to major surgeries, health insurance covers a wide range of medical expenses.
- Individual Health Insurance: Designed for a single person, this policy covers medical expenses based on the terms of the plan.
- Family Health Insurance: Extends coverage to your entire family under a single policy, making it a cost-effective option for households.
- Group Health Insurance: Typically offered by employers, this type of insurance covers employees and sometimes their families as part of a benefits package.
- Critical Illness Insurance: Provides a lump-sum payment if you’re diagnosed with a serious illness like cancer, heart disease, or stroke. This money can be used for treatment, recovery, or other expenses.
3. Auto Insurance
If you own a car, auto insurance is a must. It protects you from the financial fallout of accidents, theft, or damage to your vehicle. Depending on the policy, it can also cover injuries to others and damage to their property.
- Liability Coverage: Covers costs if you’re at fault in an accident that injures someone or damages their property.
- Crash Coverage: Pays for repairs or replacement of your car if it’s damaged in a collision.
- Full Coverage: Protects against non-collision-related incidents, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
4. Homeowners Insurance
Your home is more than just a building—it’s where you create memories and build your life. Homeowners insurance safeguards this important asset by covering damages to your home and its contents.
- Dwelling Coverage: Protects the structure of your home, including walls, roofs, and built-in appliances.
- Private Property Coverage: Covers your belongings, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Coverage: Protects you if someone sues you for injuries or damages that occur on your property.
5. Travel Insurance
Traveling is an adventure, but it comes with its own set of risks. Travel insurance ensures that you’re prepared for the unexpected, whether it’s a canceled flight, a medical emergency, or lost luggage.
- Trip Cancellation/Interruption Insurance: Reimburses you for non-refundable expenses if your trip is canceled or cut short due to unforeseen events.
- Medical Emergency Coverage: Covers medical expenses if you get sick or injured while traveling.
- Baggage and Personal Belongings Coverage: Compensates you if your luggage is lost, stolen, or damaged.
6. Business Insurance
Running a business involves taking risks, but insurance helps mitigate those risks. It saves your company from financial losses due to lawsuits, property damage, or other unforeseen events.
- General Liability Insurance: Covers legal claims related to injuries, property damage, or negligence.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Protects professionals (like doctors, lawyers, or consultants) from claims of malpractice or errors.
- Property Insurance: Covers damage to your business property, including buildings, equipment, and inventory.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Provides benefits to employees who are injured or become ill due to their work.
7. Disability Insurance
Disability insurance ensures that you can still support yourself and your family if an illness or injury prevents you from working.
- Short-Term Disability Insurance: Provides income replacement for a few months if you’re temporarily unable to work.
- Long-Term Disability Insurance: Offers coverage for extended periods, often until retirement age, if you’re unable to return to work.
8. Pet Insurance
Pets are part of the family, and their health is just as important as ours. Pet insurance helps cover the cost of veterinary care, from routine check-ups to emergency surgeries.
9. Specialty Insurance
Some risks are unique and require specialized coverage. Examples include:
- Flood Insurance: Protects against damages caused by flooding, which is typically excluded from standard homeowner’s insurance.
- Cyber Insurance: Safeguards businesses from losses due to cyberattacks or data breaches.
- Event Insurance: Covers cancellations or liabilities related to special events like weddings or concerts.

Conclusion
Insurance is more than just a financial product—it’s a lifeline. It’s about protecting what matters most, whether it’s your health, your home, your business, or your family’s future. By understanding the different types of insurance and how they work, you can make informed decisions that provide security and peace of mind.
In a world full of uncertainties, insurance is a way to take control. It’s a way to say, “No matter what happens, I’m prepared.” So, whether you’re safeguarding your family’s future with life insurance, protecting your car with auto insurance, or ensuring your business can weather any storm, insurance is the key to building a resilient and confident life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Insurance
Insurance can be a complex topic, and it’s natural to have questions about how it works, what it covers, and why it’s important. Below are some of the most common questions people have about insurance, along with clear and concise answers to help you better understand this essential financial tool.
1. What is insurance, and how does it work?
Insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company. You pay a premium—either as a lump sum or in regular installments—and in return, the insurer agrees to cover specific financial losses or risks outlined in the policy. If an insured event occurs (e.g., an accident, illness, or damage), the insurance company provides compensation or coverage as per the terms of the policy.
2. Why do I need insurance?
Insurance provides financial protection against unexpected events that could otherwise lead to significant financial hardship. It helps you manage risks, recover from losses, and maintain stability in your personal or professional life. For example, health insurance covers medical bills, auto insurance pays for car repairs after an accident, and life insurance ensures your family is financially secure if something happens to you.
3. What are the main types of insurance?
The most common types of insurance include:
- Life Insurance: Protects your family financially after your death.
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses.
- Auto Insurance: Protects against vehicle-related damages or liabilities.
- Homeowners Insurance: Covers your home and belongings.
- Travel Insurance: Protects against travel-related risks.
- Business Insurance: Safeguards businesses from financial losses.
- Disability Insurance: Provides income replacement if you’re unable to work.
4. How do I choose the right insurance policy?
Choosing the right insurance policy depends on your specific needs, lifestyle, and financial situation.
- Assess Your Risks: Identify what you need to protect (e.g., your health, car, home, or income).
- Contrast Policies: Look at different insurers, coverage options, and premiums.
- Check Coverage Limits: Ensure the policy covers enough to meet your needs.
- Read the Fine Print: Understand exclusions, deductibles, and claim procedures.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult an insurance agent or financial advisor for guidance.
5. What is a premium?
A premium is the amount you pay to the insurance company to keep your policy active. It can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually. The cost of the premium depends on factors like the type of insurance, coverage amount, your age, health, and risk level.
6. What is a deductible?
A deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles usually mean lower premiums, but you’ll pay more upfront in the event of a claim.
7. What is a claim?
A claim is a formal request you make to your insurance company for compensation or coverage after an insured event occurs. For example, if your home is damaged in a storm, you file a claim with your homeowner’s insurance to cover the repair costs. The insurer will review the claim and, if approved, provide the agreed-upon compensation.
8. What factors affect insurance premiums?
Several factors influence the cost of your insurance premiums, including:
- Risk Level: Higher-risk individuals (e.g., young drivers or smokers) pay higher premiums.
- Age and Health: Older individuals or those with pre-existing conditions may face higher health or life insurance premiums.
- Location: Areas prone to natural disasters or high crime rates may have higher premiums.
9. Can I have multiple insurance policies?
Yes, for example, you might have health insurance, auto insurance, and life insurance. However, it’s important to ensure you’re not over-insured or paying for overlapping coverage.
10. What is the term life insurance?
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specific period (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years). It’s generally more affordable and straightforward but doesn’t build cash value.
11. What is liability insurance?
Liability insurance protects you from financial losses if you’re held responsible for causing injury or damage to someone else. For example, auto liability insurance covers costs if you’re at fault in a car accident, while homeowner’s liability insurance covers injuries that occur on your property.
12. What is not covered by insurance?
Common exclusions include:
- Pre-existing Conditions: In health insurance, conditions you had before purchasing the policy may not be covered.
- Intentional Damage: Damage caused intentionally by the policyholder is not covered.
- Wear and Tear: Normal wear and tear on vehicles or property is excluded.
- Acts of War or Nuclear Hazards: These are usually excluded from most policies.
13. How do I file an insurance claim?
To file a claim, follow these steps:
- Notify Your Insurer: Contact your insurance company as soon as possible after the incident.
- Provide Documentation: Submit any required documents, such as photos, police reports, or medical records.
- Complete Claim Forms: Fill out the necessary forms provided by the insurer.
- Cooperate with the Investigation: The insurer may investigate the claim to verify its validity.
- Receive Payment: If the claim is approved, you’ll receive compensation as per the policy terms.
14. Can I cancel my insurance policy?
Yes, you can cancel your insurance policy at any time. However, you may be subject to cancellation fees or penalties, and you might not receive a full refund of your premium. It’s important to review the cancellation terms in your policy before making a decision.
15. What happens if I don’t have insurance?
Going without insurance can leave you financially vulnerable. For example:
- Without auto insurance, you could face hefty repair costs or legal penalties.
Insurance is a way to protect yourself and your loved ones from these risks.
